
As web apps have evolved to become exceptionally potent, interactive and simultaneously integrated into business operations, advanced technological development has produced sophisticated web applications that are now more susceptible than ever to external attacks. In March 2026, security professionals identified a serious defect in web applications developed using the React JS Framework. Termed the React2Shell vulnerability, this defect affects all applications built on the React JS Framework but is of particular significance for those applications using server-side rendering or using/integrating with untrusted third-party modules.
For companies using React for any of their development efforts, the React2Shell Vulnerability poses a serious risk for their businesses beyond simply being a technical problem. The React2Shell Vulnerability should not be considered just another technical bug that developers need to fix ASAP. The React2Shell Vulnerability poses a real-world risk to an organization, as it allows an attacker to gain access to their servers without using an authentication credential. Simply put, the React2Shell Vulnerability allows a cyber-criminal to enter their customer’s digital environment unhindered.
This article explains the React2Shell Vulnerability in simple terms, describes how it works, why it needs to be taken seriously, and most importantly what action can be taken now to help safeguard applications, customer data, and employee information.
What Exactly Is the React2Shell Vulnerability?
The vulnerability known as "React2Shell" is an important security risk found in 2025–26, which will be affecting React apps (especially those with server-side rendering; and third-party libraries that handle user-supplied data before being rendered). The vulnerability is much like Log4Shell (the vulnerability that affected the logging framework from Apache called Log4j) because an attacker can execute code contained in their request without needing to authenticate to your server.
Taking a look at it at its very core, the main reason for this vulnerability to exist is because of how some of these servers handle incoming requests. If an attacker was able to create a malicious payload that would appear to be completely normal, and the server does not do a good job of validating and sanitizing that request, there is a chance that the server would execute that code embedded in that request as a result of that failure to validate or sanitize.
Once the attacker gains execution access to the server, they can gain direct control over the server and, therefore, be able to;
- Execute commands
- Read or delete sensitive files
- Install backdoors
- Move deeper into your network
It is essentially the digital version of letting someone into a restricted zone simply because their request “looked fine” at first glance.
How React2Shell Works — A Simple Breakdown
While every attack varies depending on the app and infrastructure, most React2Shell exploitation paths follow a similar pattern. Here’s the flow in everyday language:
1. Reconnaissance: Finding the Weak Spot
The attacker begins by identifying websites using React, particularly those running specific unpatched libraries. They look for patterns such as server-side rendering behaviour, certain endpoints, or known flawed modules.
2. Crafting the Payload: The Hidden Weapon
The attacker creates a malicious object. This isn’t a simple text string—it’s a carefully structured payload designed to trigger unsafe deserialization on the server when React tries to process or render the request.
3. Injection: Slipping in Quietly
The malicious object is inserted into places your application likely processes without suspicion—URL parameters, API inputs, forms, or any endpoint that interacts with your React SSR logic.
4. Deserialization & Remote Code Execution
Once the server receives the payload, a vulnerable library attempts to deserialize it. Because the process is insecure, the server unintentionally executes the attacker’s code.
This is where the situation becomes dangerous.
5. Establishing a Foothold
After successful code execution, the attacker sets up a reverse shell—an open communication channel back to their machine. From here, they have continuous, interactive access to your server.
This is often only the beginning of a larger attack.
Why React2Shell Is More Than Just a Security Bug
A successful React2Shell exploitation can have far-reaching consequences. This is not limited to a single service, database, or application. The moment an attacker gains server-level access, the blast radius becomes much larger.
Here’s what’s at risk:
1. Data Exfiltration
Attackers can extract customer records, login details, financial information, internal documents—anything your server stores or has access to.
2. Full System Takeover
Once inside, they can install malware, deploy ransomware, or modify core system files. In worst cases, entire infrastructures can be held hostage.
3. Lateral Movement
One compromised server can be used as a launchpad into other parts of your network. This can lead to deeper and more complex breaches.
4. Reputational Impact
A breach linked to a known vulnerability like React2Shell can result in significant trust loss. Customers, partners, and regulators may scrutinize your security posture.
5. Financial and Legal Costs
From incident response and legal fees to regulatory fines and business downtime, the total cost of a breach can be enormous.
In short: React2Shell gives attackers the digital equivalent of your master keys. This is why organizations cannot ignore it.
A Practical Actionable Plan to Protect Your Applications
To best defend against your application(s), you should use both short-term responses and develop long-term resiliency to those threats. Remediation of vulnerabilities in React2Shell (and all other applications for that matter) is more than just applying a patch to fix the vulnerability; it's also about building your overall security posture up as high as you can.
We'll break down the steps to achieve this as follows:
1. Identify and Remediate Vulnerable Components
Prior to creating a secure environment for your application, you need to identify whatever doors and windows are open on your environment so that we can take the necessary steps to secure them. The first step in this process is to create a visual map of all of the libraries and components within your React Applications.
Audit Your Dependencies
Use tools like:
- npm audit
- Snyk
- GitHub Dependabot
Don’t stop at direct dependencies—check transitive dependencies too. Many vulnerabilities live in nested packages you might not even realize you're using.
Prioritize Patching
Once identified, patch vulnerable libraries immediately. Affected maintainers have released security updates addressing React2Shell—apply them as soon as possible.
Stay Updated
Monitor official advisories from:
- React
- Node.js
- Open-source maintainers
- CVE feeds
Being proactive keeps your team ahead of new threats.
2. Strengthen Your Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Think of your WAF as your first line of security—a gatekeeper that examines incoming requests before they reach the server.
Enable Virtual Patching
Most major WAF vendors have already released React2Shell-specific rules. These rules can detect and block exploit attempts even if your application code is still being updated.
Monitor and Log Suspicious Patterns
Look for:
- Strange serialized objects
- Unexpected nested structures
- Abnormal request patterns
- Odd user-agent strings
These are early signals of attempted exploitation.
3. Adopt Secure Coding Practices for SSR
No patch can replace a strong security culture in your development team.
Avoid Unsafe Deserialization
Review any part of your application that deserializes user-supplied input. If possible:
- Use safer data formats
- Validate inputs using strict schemas
- Avoid auto-executing serialization methods
Least Privilege Always Wins
Run your application with the lowest privileges necessary. If an attacker does break in, this minimizes what they can do.
Validate All Inputs Server-Side
Client-side validation is helpful, but never sufficient. Treat all external input as untrusted until proven otherwise.
4. Improve Monitoring and Incident Response
Even with strong defenses, visibility is essential.
Centralize Logging
Aggregate logs into a SIEM so you can detect unusual activity across your system.
Hunt for Indicators of Compromise
Be on the lookout for:
- Strange outbound connections
- Sudden spikes in resource usage
- Suspicious file creation
- Abnormal shell activity
Train & Drill Your Response Team
A plan on paper is not enough—your team must practice incident response so they can react quickly and confidently when something happens.
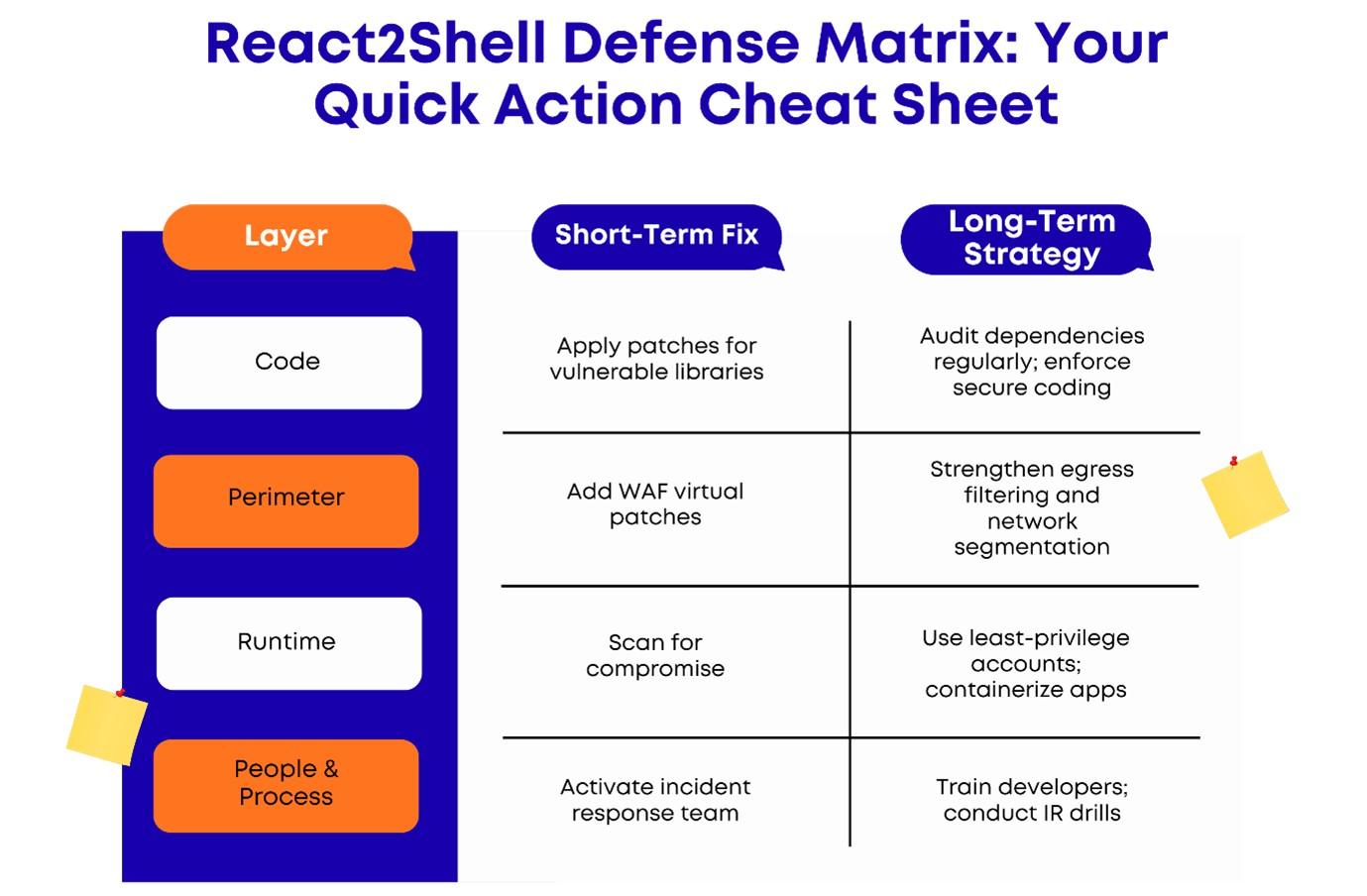
Quick Defensive Cheat Sheet
Moving Forward: Building a Proactive Security Culture
In addition to being a serious technical vulnerability, React2Shell represents something else: A harsh realization that today's modern frameworks (and their security) still present significant potential risk(s) to an organization. Furthermore, React2Shell serves as a testament to how quickly the landscape of cyber threats is changing, as well as the necessity for businesses to continue including security as part of their corporate culture via continuous processes.
The responsibility for security does not rest with a single group. Developing teams require secure code development practices, the IT department requires visibility into development, and management requires a commitment to supporting ongoing proactive budgeting for cyber security.
So, React2Shell is a perfect example of how important it is to be aware of security issues. By taking immediate action to protect yourself against React2Shell and the work done by security companies to provide solutions, you will create a stronger basis for a safe and stable digital future.
Secure Your Web Applications Against React2Shell
Get a full-stack security assessment, dependency audit, and SSR risk evaluation to safeguard your applications from this critical vulnerability.
Talk to CyberCube